
Conductive Fluoropolymers (TRC Series)
Contradictory Performance Of Conductivity And Cleanliness Achieved With The Special Technology.
We have developed a product imparted with electrical conductivity to fluoropolymer with high insulation properties, while maintaining the cleanliness and chemical resistance that are the characteristics of fluoropolymers.
Particularly for PCTFE resin that is our specialty, we have achieved to impart a stable conductivity to it for the first time in the world.
Our CNT fluoropolymer (TRC series) solves the problem with static electricity considered to be impossible to be solved so far.
What Is TRC (TOHO Resistivity Control) Series?
Features
-
- Stable Electrical Properties
- Stable electrical conductivity with little variation in volume resistivity is achieved by uniformly dispersing CNTs (carbon nanotubes) in fluoropolymer.
-
- Low Metal Elution
- The addition of a very small amount of CNT (1% or less) provides conductive performance and solves the problem of metal elution, which has been one of the issues with conventional conductive fluoropolymer materials.
This series achieved a metal elution level equivalent to that of fluoropolymers without CNTs and thereby suit applications that require extremely high cleanliness. -
- High Chemical Resistance
- This series maintains the chemical resistance that is one of the characteristics of fluoropolymers, and thereby can be used in harsh environments such as strong acids and strong alkalis.

Product Lineup
-
- TOFLON TRC-C Series [PCTFE Resin]
![TOFLON TRC-C Series [PCTFE Resin]](../../img/prodoct/trc/lineup01.jpg)
PCTFE resin with functions (antistatic and conductive) added for the first time
No degradation of mechanical properties relating to engineering of parts.
Metal elution not more than 0.1 ppb (17 metallic elements) -
- TOFLON TRC-M Series [Modified PTFE Resin (mPTFE Resin)]
![TOFLON TRC-M Series [Modified PTFE Resin (mPTFE Resin)]](../../img/prodoct/trc/lineup02.jpg)
Electrical conductivity imparted to the modified PTFE which is commonly used in applications related to semiconductor and chemical feeding.
No loss of weld strength due to addition of conductive material.
Chemical resistance equivalent to natural modified PTFE
Metal elution not more than 0.2 ppb (17 metallic elements) -
- TOFLON TRC-P Series [PTFE Resin]
- Lower volume resistivity than conventional conductive PTFE resin.
PTFE's excellent chemical resistance and low metal elution (cleanliness) are maintained(17 metallic elements).
Product Introduction
Various Performance Evaluation
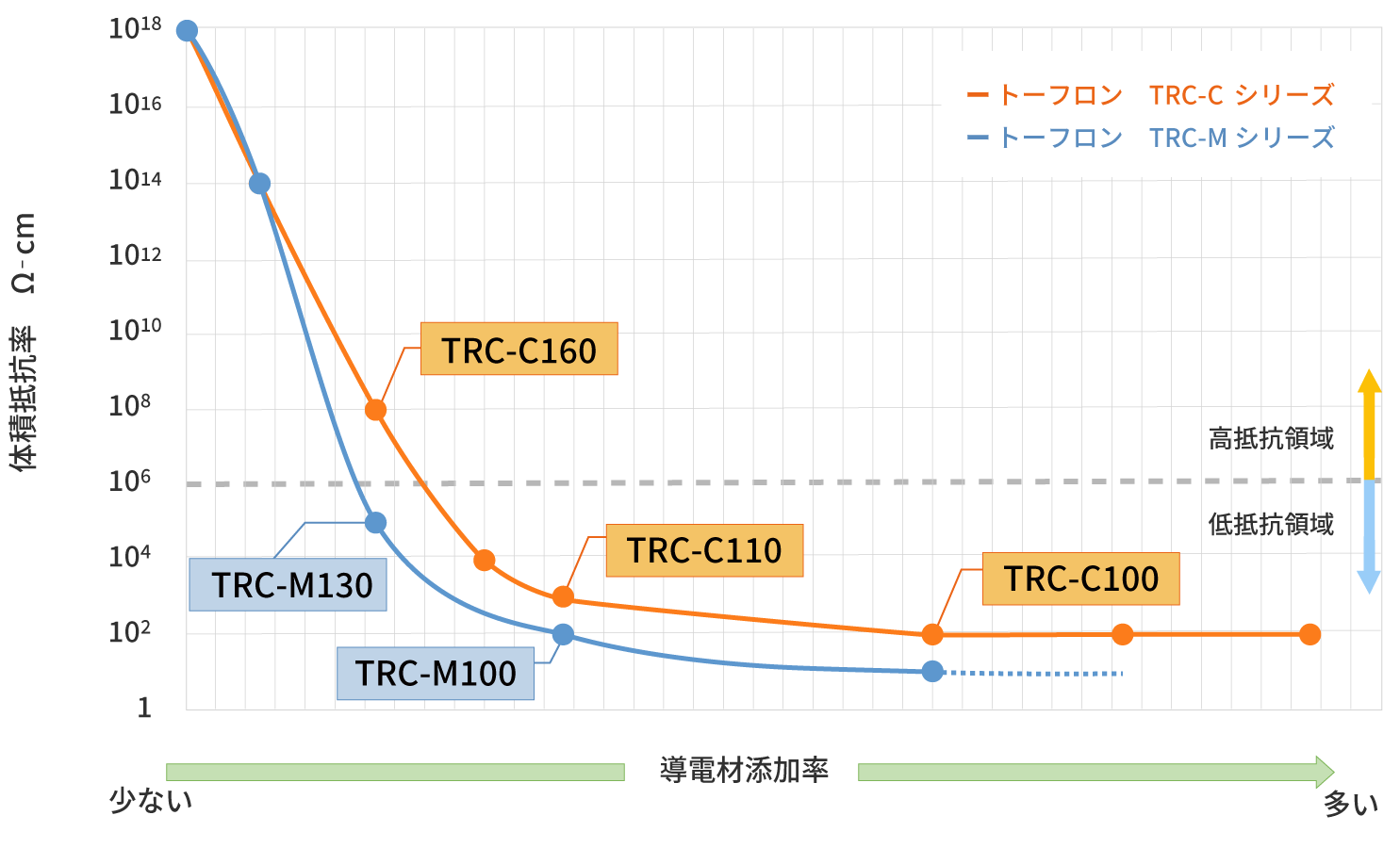
Transition of Volume Resistivity by Conductive Material Addition Rate
Metal Elution
| Measured Elements | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Ca | Fe | Mg | Na | Ni | Zn | |||
| PCTFE | Natural | 7 days (168 hours) |
0.04 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| PCTFE | TRC-C100 (100~103Ωcm) |
7 days (168 hours) |
0.02 | 0.03 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 |
| Modified PTFE | TRC-M110 (101~104Ωcm) |
7 days (168 hours) |
0.14 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| [Comparison] PFA/Carbon Fiber-Based Antistatic and Conductive Materials |
7 days (168 hours) |
2.10 | 2.10 | 2.60 | 0.22 | 0.66 | <0.01 | <0.01 | |
| DAIKIN FINETECH Control Standard | 0.50 | 5.00 | 5.00 | 0.20 | 0.50 | 5.00 | 0.50 | ||
Below Detection Limit K < 0.05 / Ti < 0.04 / Cr,Cu < 0.03 / Cd,Li < 0.01 / Co,Mn < 0.005 / Ag < 0.003 / Pb < 0.002
Chemical Resistance
| Organic Based | Acid Based | Base | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPA | Thinner | Hydrochloric Acid (37%) |
SC-2※1 | Phosphoric Acid | SPM※2 | SC-1※3 | Ammonia (28%) |
|||
| PCTFE | TRC-C100 (100~103Ωcm) |
7 days (168 hours) |
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| Modified PTFE | TRC-M110 (101~104Ωcm) |
7 days (168 hours) |
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 |
| [Comparison] PFA/Carbon Fiber-Based Antistatic and Conductive Materials |
7 days (168 hours) |
〇 | △ | △ | 〇 | × | × | 〇 | 〇 | |
| [Comparison] PTFE/Graphite-Based Antistatic and Conductive Materials |
7 days (168 hours) |
〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |
| [Comparison] PTFE/Carbon Fiber-Based Antistatic and Conductive Materials |
7 days (168 hours) |
〇 | △ | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | 〇 | |
※1 HCl:H2O2:DIW=1:1:5
※2 H2SO4:H2O2=3:2
※3 NH3:H2O2:DIW=1:1:5
Assumed Applications

-
- Driving parts such as rotating mechanisms and bending mechanisms
- Parts that are subject to frictional charging due to driving of gases and liquids
-
- Gas-liquid fluid parts
- Piping parts that become electrically charged unless the flow velocity is reduced, and nozzle parts that cannot uniformly apply liquid if the liquid becomes electrically charged
-
- Substitute for metals
- Parts that were conventionally coated with metal but need to be coated with resin to achieve higher cleanliness
